Assessment of water quality using multivariate analysis in estuaries of the Gulf of Fonseca, Honduras
Calidad de agua en los esteros del Golfo de Fonseca
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.25268/bimc.invemar.2023.52.1.1181Keywords:
water quality, estuaries, Gulf of Fonseca, Pacific Honduras, physicochemical variablesAbstract
Excessive nutrient enrichment is a contributing factor to the degradation of estuarine ecosystems, influenced by anthropogenic activities and natural processes. The objective of this study was to describe each of the environmental variables in eight estuaries of the Gulf
of Fonseca over time and to analyze them using multivariate statistical techniques. Water quality data were collected from eight estuaries in the Gulf of Fonseca that included seven environmental variables between 2000-2015. They were analyzed using water quality
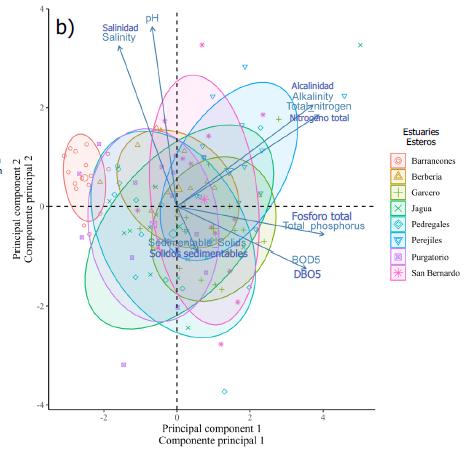
criteria, principal component analysis (PCA) and cluster analysis. The PCA resulted in three components that explained 72.6 % of the total variance. The analyses indicated that the San Bernardo, La Jagua, El Garcero, Perejiles, Pedregales and Berbería estuaries had high levels
of total nitrogen, total phosphorus, Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD5), settleable solids and alkalinity, constituting the group with the highest concentration of nutrients. The Purgatorio and Barrancones estuaries had optimal water quality levels and therefore constituted the
group with the lowest concentration of nutrients. It is necessary to take preventive measures to encourage the development of aquatic life by guiding effective regulation and systematic control of effluents and tributaries to achieve an effective coastal service to support future
management and restoration efforts.
References
Alexakis, D. 2011. Assessment of water quality in the Messolonghi–Etoliko and Neochorio region (West Greece) using hydrochemical and statistical analysis methods. Environ. Monit. Assess., 182: 397–413.
ANDAH, Asociación Nacional de Acuicultores de Honduras. 2020. Camarón de Honduras. Industria camaronera. https://andah.hn/camaron-de-honduras/
Araujo, A. V., C.O. Dias and S.L.C. Bonecker. 2017. Effects of environmental and water quality parameters on the functioning of copepod assemblages in tropical estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci., 194: 150–161.
Barakat, A., M. El Baghdadi, J. Rais, B. Aghezzaf and M. Slassi. 2016. Assessment of spatial and seasonal water quality variation of Oum Er Rbia River (Morocco) using multivariate statistical techniques. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res., 4: 284–292.
Barletta, M., A.R.A. Lima and M.F. Costa. 2019. Distribution, sources and consequences of nutrients, persistent organic pollutants, metals and microplastics in South American estuaries. Sci. Total. Environ., 651: 1199–1218.
Barraza-Guardado, R.H., J. Arreola-Lizárraga, M. López-Torres, R. Casillas-Hernández, A. Miranda-Baeza, F. Magallón-Barrajas and C. Ibarra-Gámez. 2013. Effluents of shrimp farms and its influence on the coastal ecosystems of Bahia de Kino, Mexico. Sci. World J., 2013.
Bartlett, M. S. 1951. The effect of standardization on a χ2 approximation in factor analysis. Biometrika., 38: 337–344.
Benessaiah, K. and R. Sengupta. 2014. How is shrimp aquaculture transforming coastal livelihoods and lagoons in Estero Real, Nicaragua? The need to integrate social-ecological research and ecosystem-based approaches. Environ. Manage., 54: 162–179.
Blair, M., P. Ortiz, M. Argueta y L. Romero. 2019. Calidad del agua en Honduras: 394-416. En Roldan. G. et al. (Ed.) Calidad de agua en las Américas, riesgos y oportunidades. UNESCO, París.
Boyd, C.E. 2003. Guidelines for aquaculture effluent management at the farm-level. Aquaculture, 226: 101–112.
Boyd, C. and D. Gautier. 2000. Effluent composition and water quality standards–Responsible Seafood Advocate. Glob. Aquac. Advocate, 3: 61–66.
Boyd, C. and B. Green. 2002. Coastal water quality monitoring in shrimp farming areas: An example from Honduras. World Bank, NACA, WWF and FAO Consort. Progr. Shrimp Farming Environ. 29 p.
Boyd, C.E., C.S. Tucker and B. Somridhivej. 2016. Alkalinity and hardness: Critical but elusive concepts in aquaculture. J. World Aquac. Soc., 47: 6–41.
Breitburg, D.L., D.W. Hondorp, L.A. Davis and R.J. Díaz. 2008. Hypoxia, nitrogen, and fisheries: Integrating effects across local and global landscapes. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci., 1: 329–349.
Brockmeyer, B. and A. Spitzy. 2011. Effects of sugar cane monocultures on origin and characteristics of dissolved organic matter in the Manguaba lagoon in northeast Brazil. Org. Geochem., 42: 74–83.
Bugica, K., B. Sterba-Boatwright and M.S. Wetz. 2020. Water quality trends in Texas estuaries. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 152: 110903.
Bull, E. G., C.L.N. de da Cunha and A.C. Scudelari. 2021. Water quality impact from shrimp farming effluents in a tropical estuary. Water Sci. Technol., 83: 123–136.
Carbonell, G., C. Ramos and J.V. Tarazona. 1998. Metals in shrimp culture areas from the Gulf of Fonseca, Central America. I. Sediments. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 60: 252–259.
Cardoso-Mohedano, J. G., F. Páez-Osuna, F. Amezcua-Martínez, A.C. Ruiz-Fernández, G. Ramírez-Reséndiz and J.A. Sánchez-Cabeza. 2016. Combined environmental stress from shrimp farm and dredging releases in a subtropical coastal lagoon (SE Gulf of California). Mar. Pollut. Bull., 104: 83–91.
Cardoso-Mohedano, J. G., J. Lima-Rego, J-A. Sánchez-Cabeza, A-C. Ruiz-Fernández, J. Canales-Delgadillo, E.I. Sánchez-Flores and F. Páez-Ozuna. 2018. Sub-tropical coastal lagoon salinization associated to shrimp ponds effluents. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci., 203: 72–79.
Carrasco, G., J.-S. Molina, M.-C. Patiño-Alonzo, M. Castillo, M.-P. Vicente-Galindo and M.-P. Galindo-Villardón. 2019. Water quality evaluation through a multivariate statistical HJ-Biplot approach. J. Hydrol., 577: 123993.
Carrera, D., P. Guevara, L. Tamayo y D. Guallichico. 2015. Análisis multivariado de las aguas de la subcuenca del río Ambi en época de estiaje y su relación con la calidad desde el punto de vista agrícola. Congr. Cienc. Tecnol. Espe, 10: 123–129.
CATIE. 2008. Formulación del plan de manejo y acciones estratégicas para el manejo integral y desarrollo territorial de la microcuenca del río Soledad, microcuenca del río Texiguat y cuenca Baja del Río Choluteca, PREVDA-HON/SERV/005-07. Centro Agron. Trop. Invest. Enseñ.
Caviedes-Sánchez, V., L. Rivera-Peñalva, A. Rodríguez y J. Navas-Parejo. 2016. Estado del manejo integrado de los espacios y recursos marinos y costeros de Honduras. https://diciht.unah.edu.hn/investigacion-cientifica/becas-i-d-i/proyectos-especiales-de-investigacion-cientifica/manejo-integrado-espaciosrecursos-marinos-y-costeros/
CHM. 2017. Propuesta de diseño e implementación del corredor biológico del golfo de Fonseca, Nicaragua. https://docplayer.es/75859382-Propuesta-dediseno-e-implementacion-del-corredor-biologico-del-golfo-de-fonseca-nicaragua.html
Clark, K. E., V. Bravo, S. Guiddings, K. Davis, G. Pawlak, M. Torres, A. Adelson, C. Cesar-Ávila, X. Boza and R. Collin. 2022. Land use and land cover shape river water quality at a continental Caribbean land-ocean interface front. Water, 4.
Clarke, K. R., R.N. Gorley, P.J. Somerfield and R.M. Warwick. 2014. Change in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation. (PRIMER-E: Plymouth). 262 p.
CONAMA. 2004. Guía CONAMA para el establecimiento de las normas secundarias de calidad ambiental para aguas continentales superficiales y marinas. https://www.u-cursos.cl/forestal/2009/0/PR010-1/1/material_docente/bajar?id=480218&bajar=1
Cooke, S.J., C. Paukert and Z. Hogan. 2012. Endangered river fish: factors hindering conservation and restoration. Endanger. Species Res., 17: 179–191.
Costa, C.R., M.F. Costa, D.V. Dantas and M. Barletta. 2018. Interannual and seasonal variations in estuarine water quality. Front. Mar. Sci., 5: 301.
Cybulski, J.D., S. Husa, N. Duprey, B. Mamo, T. Tsang, M. Yasuhara, J. Xie, J-W. Qiu, Y. Yokoyama and D. Baker. 2020. Coral reef diversity losses in China’s greater bay area were driven by regional stressors. Sci. Adv., 6.
Darwall, W.R. T. and J. Freyhof. 2015. Lost fishes, who is counting? The extent of the threat to freshwater fish biodiversity: 1.36. In Closs, G., M. Krkosek and J. Olden (Eds.) Conservation of freshwater fishes. Cambridge. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139627085.002
del Cid Gómez, J.A. y J.D. Cáceres. 2017. Variación de la línea de costa en la aldea de Cedeño, y cartografía de amenaza ante marejadas y ascenso del nivel del mar. Portal Cienc., 87–102. https://doi.org/10.5377/PC.V13I0.5969
Delgado, A.C.P. 2019. Índice de vulnerabilidad ante efectos del cambio climático: Choluteca, Honduras. Población y Des. Argon. Camin., 15: 52–61.
Dewalt, B.R., P. Vergne and M. Hardin. 1996. Shrimp aquaculture development and the environment: People, mangroves and fisheries on the Gulf of Fonseca, Honduras. World Dev., 24: 1193–1208.
Duque, G., D.E. Gamboa-García, A. Molina and P. Cogua. 2022. Influence of water quality on the macroinvertebrate community in a tropical estuary (Buenaventura Bay). Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag., 18: 796–812.
Fernandes, L.L., V.P. Rao, P.M. Kessarkar and S. Suresh. 2018. Estuarine turbidity maximum in six tropical minor rivers, central west coast of India. Hydrol. Res., 49: 1234–1254.
Galal-Gorchev, H., G. Ozolins and X. Bonnefoy. 1993. Revision of the WHO guidelines for drinking water quality. Ann. Inst. Super. Sanit., 29: 335–345.
Giridharan, L., T. Venugopal and M. Jayaprakash. 2009. Assessment of water quality using chemometric tools: A case study of river cooum, South India. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 56: 654–669.
Gladstone, S. 2002. Contaminación por plaguicidas en las cuencas hidrográficas que desembocan en el golfo de Fonseca y oportunidades para su prevención y mitigación. Informe Final, golfo de Fonseca, Honduras.
http://www.chmhonduras.org/phocadownloadpap/CODDEFFAGOLF/Estudios/Estudio de
contaminacion por Plaguicidas en las Cuencas del golfo de Fonseca.pdf
Gonzales-Bermúdez, G.A., V.E. Jara-Calderón y J.A. Garro-Fallas. 2016. El golfo de Fonseca, más que un conflicto político. La perspectiva desde los actores locales y pobladores costeros. Pensam. Actual., 16: 147–161.
Green, B. and G.H. Ward. 2011. Ultimate biochemical oxygen demand in semi-intensively managed shrimp pond waters. Aquaculture, 319: 253–261.
Hernández-Cornejo, R. and A. Ruiz-Luna. 2000. Development of shrimp farming in the coastal zone of southern Sinaloa (Mexico): operating characteristics, environmental issues, and perspectives. Ocean Coast. Manag., 43: 597–607.
Hortle, K. 2009. Fishes of the Mekong-how many species are there? Taxonomy., 15: 4–12.
IANA. 2019.Calidad de agua en las Américas, riesgos y oportunidades. Inf. final. Red Interam. Acad. Cienc. http://grupomontevideo.org/ndca/caaguas/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/wb09.pdf
Jones, A.B., M.J. O’Donohue, J. Udy and W.C. Dennison. 2001. Assessing ecological impacts of shrimp and sewage effluent: Biological indicators with standard water quality analyses. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci., 52: 91–109.
Kaiser, H. F. 1970. A second-generation little jiffy. Psychom, 35: 401–415.
Karydis, M. and D. Kitsiou. 2013. Marine water quality monitoring: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 77: 23–36.
Kazi, T.G., M.B. Arain, M.K. Jamali, N. Jalbani, H.I. Afridi, R.A. Sarfraz, J.A. Baig and A-Q. Shah. 2009. Assessment of water quality of polluted lake using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 72: 301–309.
Kitsiou, D. and M. Karydis. 2011. Coastal marine eutrophication assessment: A review on data analysis. Environ. Int., 37: 778–801.
Lotze, H. K., H. Lenihan, B. Bourque, R. Bradbury, R. Cooke, M. Kay, S. Kidwell, M. Kirby, Ch. Peterson and J. Jackson. 2006. Depletion degradation, and recovery potential of estuaries and coastal seas. Science, 80-312: 1806–1809.
Mateus, C., C.A. Guerrero, G. Quezada, D. Lara and V. Ochoa-Herrera. 2019. An integrated approach for evaluating water quality between 2007–2015 in Santa Cruz Island in the Galapagos Archipelago. Water, 11: 1–28.
Metcalf, J.S., S.A. Banack, R.A. Wessel, M. Lester, J.G. Pim, J.R. Cassani and P.A. Cox. 2021. Toxin analysis of freshwater cyanobacterial and marine harmful algal blooms on the west coast of Florida and implications for estuarine environments. Neurotox. Res., 39: 27–35.
Miller, J.J., M. Maher, E. Bohaboy, C.S. Friedman and P. McElhany. 2016. Exposure to low pH reduces survival and delays development in early life stages of Dungeness crab (Cancer magister). Mar. Biol., 163: 1–11.
Ministerio de Ambiente de Ecuador. 2015. Acuerdo 097-A, Anexo 1 del Libro VI del Texto Unificado de Legislación Secundaria del Ministerio del Ambiente: Norma de Calidad Ambiental y de Descarga de Efluentes al Recurso Agua. MAE. https://www.gob.ec/sites/default/files/regulations/2018-09/Documento_ Registro-Oficial-No-387-04-noviembre-2015_0.pdf
Mitra, S., S. Ghosh, K. Satpathy, B. Bhattacharya, S. Sarkar, P. Mishra and P. Raja. 2018. Water quality assessment of the ecologically stressed Hooghly River Estuary, India: A multivariate approach. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 126: 592–599.
Montoya-Suárez, O. 2007. Aplicación del análisis factorial a la investigación de mercados. Sci. Tech., 13: 281–286.
Mudge, S.M., J.D. Icely and A. Newton. 2007. Oxygen depletion in relation to water residence times. J. Environ. Monit., 9: 1194–1198.
Nasiha, H.J., P. Shanmugam and R. Sundaravadivelu. 2019. Estimation of sediment settling velocity in estuarine and coastal waters using optical remote sensing data. Adv. Sp. Res., 63: 3473–3488.
Nichols, F.H., J.E. Cloern, S.N. Luoma and D.H. Peterson. 1986. The modification of an estuary. Science, 231: 567–573.
Oketola, A.A., S.M. Adekolurejo and O. Osibanjo. 2013. Water quality assessment of River Ogun using multivariate statistical techniques. J. Environ. Prot., 4: 466–479.
OMS. 2019. Agua potable. Organización Mundial de la Salud. https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/drinking-water
Orozco, C., A. Pérez, M. González, F. Rodríguez y J. Alfayate. 2005. Contaminación ambiental. Una visión desde la química. Thomson. 680 p.
Osorto, M. H., E. Ulloa, F. Álvarez, E. Rodríguez, F. Giménez y V. Merlo. 2017. Comparación de dos comunidades biológicas marinos costeros en Cedeño, Choluteca. Portal Cienc., 51–70. https://doi.org/10.5377/PC.V12I0.5517
Páez-Osuna, F., A. Gracia, F. Flores-Verdugo, L.P. Lyle-Fritch, R. Alonso Rodríguez, A. Roque and A.C. Ruiz-Fernández. 2003. Shrimp aquaculture development and the environment in the Gulf of California ecoregion. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 46: 806–815.
Palma, P., P. Alvarenga, V. Palma, R.M. Fernández, M.V.M Soares and I. Barbosa. 2009. Assessment of anthropogenic sources of water pollution using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Alqueva’s reservoir, Portugal. Environ. Monit. Assess., 165: 539–552.
Palmer, T.A. and P.A. Montagna. 2015. Impacts of droughts and low flows on estuarine water quality and benthic fauna. Hydrobiology, 753: 111–129.
Pérez, R., F. Riveiro, M. Jiménez–Noda, L. Manganiello, C. Vega, R. Covad y J. Moreno. 2017. Evaluación de la calidad del agua en un humedal de agua salada del Caribe. Rev. Ing. UC., 24: 417–427.
Pérez-Castillo, A.G. y A. Rodríguez. 2008. Índice fisicoquímico de la calidad de agua para el manejo de lagunas tropicales de inundación. Rev. Biol. Trop., 56: 1905–1918.
Picado-Barboza, J. 2015. Distribución espacial y temporal de la salinidad en la columna de agua del sector estuarino del Humedal Nacional Térraba Sierpe, Costa Rica. Rev. Biol. Trop., 63: 75–96.
Pineda-Portillo, N. 2001. Análisis cartográfico de la cuenca del río Choluteca. Rev. Cartogr., 72: 7–24.
Promangle. 2002. Zonificación de los bosques de mangle del golfo de Fonseca, Honduras, C.A. Informe Final, Manejo y conservación de los manglares del golfo de Fonseca. https://www.itto.int/files/itto_project_db_input/2271/Technical/pd44-95-2 rev 3 (F) s_Zonificacion de los bosques de mangle del golfo de Fonseca_S.pdf
Rice, E., R. Baird, A. Eaton and L. Clesceri. 2012. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association. 724 p.
Rivera-Castro, A.C., J. Letelier-Pino, B. Acevedo-Pizarro, T. Tobar-Correa, C. Torres-Lepe, A. Cataldo-Figueroa, A. Rudolph-Geisse y M. Rivera-Castro. 2020. Calidad de agua del estero El Sauce, Chile Central. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient., 36: 261–273.
Rodríguez-Grimón, R.O., J. Valenzuela-Cobos, J. Erazo-Delgado, I. Terán-Narváez, M.F. Garces-Moncayo, A. Grijalva-Endara and J.M. Tierra-Arévalo. 2021. First study of water quality in the San Camilo and Mojahuevo estuaries located in Guayas for being used in aquaculture. Acta Period. Technol., 55–62. https://doi.org/10.2298/APT2152055R
Rojo, C., D. Lumbi, A. Aguilar, K. Palacios, K. Osorio and P. Ruiz. 2021. The river influence controls water quality and spatio-temporal microalgal distribution in Pacific estuaries (Padre Ramos and Salinas Grandes) of Nicaragua. Water, 13: 1712.
Rovira, D., R. Castillo y V. Espinosa. 2015. Parámetros fisicoquímicos y microbiológicos como indicadores de la calidad de las aguas de la subcuenca baja del Río David, Provincia de Chiriquí, Panamá. David, Panamá. http://www.oteima.ac.pa/nueva/investigaciones/Parámetros Físico-químico listo.pdf
Samboni-Ruiz, N.E., Y. Carvajal-Escobar y J.C. Escobar. 2007. Revisión de parámetros fisicoquímicos como indicadores de calidad y contaminación del agua. Rev. Ing. Invest., 27: 172–181.
Sarma, V.V.S.S., S.N.M. Gupta, P.V.R. Babu, T. Acharya, N. Harikrishnachari, K. Vishnuvardhan, N.S. Rao, N.P.C. Reddy, V.V. Sarma, Y. Sadhuram, T.V.R. Murty and M.D. Kumar. 2009. Influence of river discharge on plankton metabolic rates in the tropical monsoon driven Godavari estuary, India. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci., 85: 515–524.
Sasa, M., X. Armengol, F. Bonilla, F. Mesquita-Joanes, R. Piculo, C. Rojo, R. Rueda and J. Monroe. 2015. Seasonal wetlands in the Pacific coast of Costa Rica and Nicaragua: environmental characterisation and conservation state. Limnetica, 29: 1–16.
Shin, J. Y., F. Artigas, C. Hobble and Y.S. Lee. 2013. Assessment of anthropogenic influences on surface water quality in urban estuary, northern New Jersey: Multivariate approach. Environ. Monit. Assess., 18: 2777–2794.
Singh, K.P., A. Malik, D. Mohan and S. Sinha. 2004. Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India) a case study. Water Res., 38: 3980–3992.
Soto, L., C. Andara y E. Sánchez. 2012. Informe de evaluación de la actividad pesquera en el golfo de Fonseca, Honduras en los periodos del 2004-2010. Informe final, golfo de Fonseca, Honduras. https://docplayer.es/24700929-Informe-de-evaluacion-de-la-actividad-pesquera-en-el-golfo-de-fonseca-honduras.html
Stanley, D. 2002. Science and society in the Gulf of Fonseca the changing history of mariculture in Honduras. World Bank, NACA, WWF, FAO Consort. Progr. Shrimp Farm. Environ. 39 p.
Stram, D.L., C.R. Kincaid and D.E. Campbell. 2005. Water quality modeling in the Rio Chone estuary. J. Coast. Res., 21: 797–810.
Vásquez, Y., O. Martínez y D. Obando. 2021. Plan comunitario de resiliencia al cambio climático: CASERÍOS: Cayanini, La Anona, El Nancital El Corpus, Choluteca Honduras. Informe final, Honduras. https://cgspace.cgiar.org/handle/10568/115917
Vega, M., R. Pardo, E. Barrado and L. Debán. 1998. Assessment of seasonal and polluting effects on the quality of river water by exploratory data analysis. Water Res., 32: 3581–3592.
Veríssimo, H., M. Lane, J. Patricio, S. Gamito and J.C. Marques. 2013. Trends in water quality and subtidal benthic communities in a temperate estuary: Is the response to restoration efforts hidden by climate variability and the Estuarine Quality Paradox? Ecol. Indic., 24: 56–67.
Ward, G.H. 2000. Effects of shrimp farming on the hydrography and water quality of El Pedregal and San Bernardo estuaries, Gulf of Fonseca, Honduras. Res. Rep., 1–32.
Ward, J.H. 1963. Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. J. Am. Stat. Assoc., 58: 236–244.
Weisberg, S.B., N. Bednaršek, R. Feely, F. Chan, A. Boehm, M. Sutula, J. Ruesink, B. Hales, J. Largier and J. Newton. 2016. Water quality criteria for an acidifying ocean: Challenges and opportunities for improvement. Ocean Coast. Manag., 126: 31–41.
Weitnauer, E., M. Berrocal, J.A. Leiva y J. Segovia. 2018. Informe de calidad de agua superficial de la bahía de La Unión en El Salvador y la bahía de Chismuyo. Informe Final, golfo de Fonseca. https://issuu.com/delacuencaalacostaicwl/docs/informe_calidad_de_agua_bahias_de_l
Wetz, M.S., K.C. Hayes, K.V.B. Fisher, L. Price and B. Sterba-Boatwright. 2016. Water quality dynamics in an urbanizing subtropical estuary (Oso Bay, Texas). Mar. Pollut. Bull., 104: 44–53.
Yin, K., Z. Lin and Z. Ke. 2007. Temporal and spatial distribution of dissolved oxygen in the Pearl River Estuary and adjacent coastal waters. Cont. Shelf Res., 24: 1935–1948.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Marco Herminio Osorto Nuñez

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

