Publicado 2024-07-02
Palabras clave
- bioestimulantes,
- agroquímicos,
- metabolitos algales/macroalgales
Cómo citar
Derechos de autor 2024 Angela Pacheco

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0.
Resumen
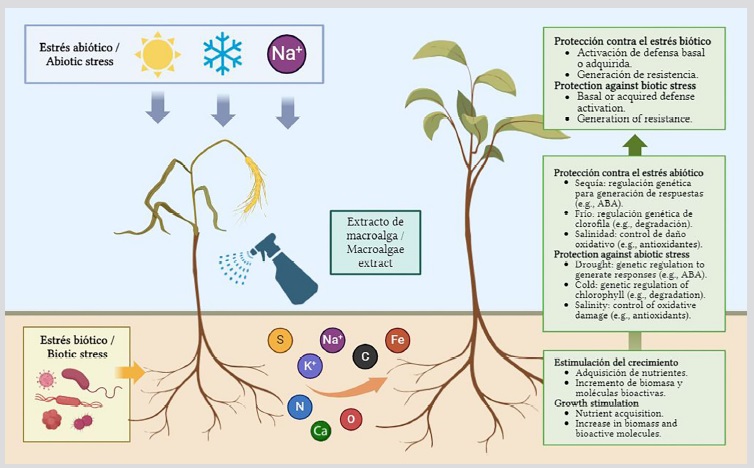
El empleo de compuestos bioactivos extraídos de macroalgas en forma de formulaciones agrícolas representa una tecnología emergente con gran potencial para reducir la dependencia de agroquímicos sintéticos. Al presente, los extractos de algas marinas se consideran
un recurso sostenible debido a su carácter biodegradable. En esta revisión se discute su potencial para reemplazar o reducir a una variedad de moléculas sintéticas en cultivos económicamente importantes, tales como fertilizantes sintéticos nitrogenados y fosfatados, reguladores del crecimiento hormonales sintéticos y plaguicidas organoclorados y organofosforados. Por la presencia de una extensa gama
de sustancias bioactivas ya registradas en ciertas algas se prevén como buenos candidatos para la producción de bioformulaciones vegetales.
En este sentido, el aprovechamiento comercial y biotecnológico de las macroalgas podría beneficiar la economía local. Sin embargo, pese
a todo el potencial de las algas existe muy poca información de su contenido metabolómico o químico total. Esta revisión bibliográfica
resume información que propone el uso de las macroalgas Kappaphycus. alvarezii, Acanthophora spicifera e Hypnea spinella dentro del
sector agrícola ecuatoriano como alternativa para la reducción de pesticidas.
Descargas
Citas
- Agarwal, P., M. Dangariya and P. Agarwal. 2021. Seaweed extracts: Potential biodegradable, environmentally friendly resources for regulating plant defense. Algal Res., 58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2021.102363
- Alcántara, J.D. and N. Lázaro-Llanos. 2020. Mineral availability, dietary fiber contents, and short-chain fatty acid fermentation products of Caulerpa lentillifera and Kappaphycus alvarezii seaweeds. Komun. Kimika, 31(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.26534/kimika.v31i1.1-10
- Ali, O., A. Ramsubhag and J. Jayaraman. 2021. Biostimulant properties of seaweed extracts in plants: Implications towards sustainable crop production. Plants, 10(3): 1–27. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10030531
- Ali, O., A. Ramsubhag and J. Jayaraman. 2022. Transcriptome-wide modulation by Sargassum vulgare and Acanthophora spicifera extracts results in a prime-triggered plant signalling cascade in tomato and sweet pepper. AoB Plants, 14(6): 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1093/aobpla/plac046
- Al-Shatri, A.H., N.M. Pakyürek and A. Yaviç. 2020. Effect of seaweed application on nutrient uptake of strawberry cv. Albion grown under the environmental conditions of northern Iraq. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res., 18(1), 1267–1279. https://doi.org/10.15666/aeer/1801_12671279
- Aminah, A. and G. K. Xiren. 2017. Proximate composition and total amino acid composition of Kappaphycus alvarezii found in the waters of Langkawi and Sabah, Malaysia. Int. Food Res. J., 24(3): 1255–1260.
- Ammar, G., M. Ashour and S. M. Hassan. 2022. Enhancing potato production by applying commercial seaweed extract (TAM®) biostimulant under field conditions. JAAR, 27(3), 492-504. https://doi.org/10.21608/jalexu.2022.155031.1077
- Ashour, M., S. M. Hassan, M. E. Elshobary, G. A. G. Ammar, A. Gaber, W. F. Alsanie, A. T. Mansour and R. El-shenody. 2021. Impact of commercial seaweed liquid extract (Tam®) biostimulant and its bioactive molecules on growth and antioxidant activities of hot pepper (Capsicum annuum). Plants, 10(6), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10061045
- Augusto, A., T. Simões, R. Pedrosa and S. F. J. Silva. 2016. Evaluation of seaweed extracts functionality as post-harvest treatment for minimally processed Fuji apples. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol., 33, 589-595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2015.10.004
- Banakar, S., N., M. K. Prasanna Kumar, H. B. Mahesh, P. B. Parivallal, M. E. Puneeth, C. Gautam, D. Pramesh, T. N. Shiva Kumara, T. R. Girish, S. Nori and S. S. Narayan. 2022. Red-seaweed biostimulants differentially alleviate the impact of fungicidal stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Scient. Rep., 12(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-10010-8
- Baskararaj, S., T. Panneerselvam, S. Govindaraj, S. Arunachalam, P. Parasuraman, S. R. K. Pandian, M. Sankaranarayanan, U. P. Mohan, P. Palanisamy, V. Ravishankar and S. Kunjiappan. 2020. Formulation and characterization of folate receptor-targeted PEGylated liposome encapsulating bioactive compounds from Kappaphycus alvarezii for cancer therapy. 3 Biotech, 10(3): 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-2132-7
- Brotosudarmo, T., H. Heriyanto, Y. Shioi, I. Indriatmoko, M. Setya, R. Indrawati and L. Limantara. 2018. Composition of the main dominant pigments from potential two edible seaweeds. Philipp J. Sci., 147(1): 47–55.
- Cai, J. 2021. Global status of seaweed production, trade and utilization. Seaweed Innovation Forum Belize (28 May 2021). Available at: https://www.competecaribbean.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/Global-status-of-seaweed-production-trade-and-utilization-Junning-Cai-FAO.pdf
- Cai, J., A. Lovatelli, J. Aguilar-Manjarrez, L. Cornish, L. Dabbadie, A. Desrochers, S. Diffey, E. Garrido Gamarro, J. Geehan, A. Hurtado, D. Lucente, G. Mair, W. Miao, P. Potin, C. Przybyla, M. Reantaso, , R. Roubach, M. Tauati and X. Yuan. 2021. Seaweeds and microalgae: an overview for unlocking their potential in global aquaculture development. FAO Fish. Aquacult. Circ., 1229. FAO. https://doi.org/10.4060/cb5670en
- Cokrowati, N., Y. Risjani, S. Andayani and M. Firdaus. 2023. Phytohormone quantification of Kappaphycus alvarezii at different cultivated ages. J. Penyuluh.Perikan. Kelaut., 28(1): 89–96.
- Dash, A., D. Samant, D. K. Dash, S. N. Dash and K. N. Mishra. 2021. Influence of Ascophyllum nodosum extract, homobrassinolide and triacontanol on fruit retention, yield and quality of mango. J. Environ. Biol., 42(4), 1085–1091. https://doi.org/10.22438/jeb/42/4/MRN-1541
- Dziugieł, T. and W. Wadas. 2020. Effect of plant biostimulants on macronutrient content in early crop potato tubers. Agronomy, 10(8), 1202. https://doi.
- org/10.3390/agronomy10081202
- Elsharkawy, G., A., H. A. H. Ibrahim, A. H. Salah, M. Akrami, H. M. Ali and D. Y. Abd-Elkader. 2021. Early and total yield enhancement of the globe
- artichoke using an ecofriendly seaweed extract-based biostimulant and pk fertilizer. Agronomy, 11(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11091819
- Ertani, A., O. Francioso, A. Tinti, M. Schiavon, D. Pizzeghello and S. Nardi. 2018. Evaluation of seaweed extracts from Laminaria and Ascophyllum
- nodosum spp. As biostimulants in Zea mays L. using a combination of chemical, biochemical and morphological approaches. Front. Plant Sci. ,
- (April). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00428
- Espinosa-Antón, A., A., J. F. Zamora-Natera, P. Zarazúa-Villaseñor, F. Santacruz-Ruvalcaba, C. V. Sánchez-Hernández, E. Águila Alcántara, M. I. Torres-
- Morán, A. P. Velasco-Ramírez and R. M. Hernández-Herrera. 2023. Application of seaweed generates changes in the substrate and stimulates the
- growth of tomato plants. Plants, 12(7), 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12071520
- FAO. 2022. Thinking about the future of food safety–A foresight report. FAO. https://doi.org/10.4060/cb8667en
- Fatimah, S., H. Alimon and N. Daud. 2018. The effect of seaweed extract (Sargassum sp) used as fertilizer on plant growth of Capsicum annum (chilli)
- and Lycopersicon esculentum (tomato). Indones. J. Sci. Technol., 3(2), 115–123. https://doi.org/10.17509/ijost.v3i2.12755
- Flórez-Jalixto, M., D. Roldán-Acero, J. R. Omote-Sibina and A. Molleda-Ordóñez. 2021. Biofertilizers and biostimulantsfor agricultural and aquaculture
- use: Bioprocesses applied to organic by-products of the fishing industry. Sci. Agropec., 12(4): 635-651. https://doi.org/10.17268/sci.agropecu.2021.067
- Ganesan, M., R. Kannan, K. Rajendran, C. Govindasamy, P. Sampathkumar and L. Kannan. 1991. Trace metals distribution in seaweeds of the Gulf of
- Mannar, Bay of Bengal. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 22(4): 205–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-326X(91)90472-5
- Gara, A. B., N. Hammami, R. Chaaben, A. El Feki, F. P. Pattie, K. Belghith and I. Dahech. 2022. Inhibition of key digestive enzymes related to diabetes
- and protection of β -cell and liver- kidney functions by Hypnea spinella sulfated polysaccharide in diabetic rats. Res Sq.
- González-Giro, Z., P. L. Batista-Corbal, Y. González-Pérez, E. Rodríguez-Leblanch y E. Marcos-Albear. 2018. Evaluación de la fitotoxicidad de un
- extracto acuoso del alga Padina gymnospora (Kützing) sobre semillas de Lactuca sativa L. Biot. Veg., 18(3): 181–188.
- Guillén, P. O., P. Motti, S. Mangelinckx, O. De Clerck, P. Bossier and S. Van Den Hende. 2022. Valorization of the chemical diversity of the tropical
- red seaweeds Acanthophora and Kappaphycus and their applications in aquaculture: A review. Front. Mar. Sci., 9: 1–21. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2022.957290
- Hamzah, L., M., H. K. Hussein and F. K. M. Al-Waili. 2023. Response of sour orange seedlings to spraying with magnesium and seaweed extract Kelpak 40b. April. https://connectjournals.com/pages/articledetails/toc036548
- Hassan, S., M., M. Ashour, N. Sakai, L. Zhang, H. A. Hassanien, A. Gaber and G. A. G. Ammarr. 2021. Impact of seaweed liquid extract biostimulant on growth, yield, and chemical composition of cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Agriculture, 11(4), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11040320
- Illera-Vives, M., S. Seoane-Labandeira, M. Fernández-Labrada and M. E. López-Mosquera. 2020. Agricultural uses of seaweed. 591-612. En: Torres, M. D., S. Kraan and H. Dominguez (Eds). Sustainable seaweed technologies: cultivation, biorefinery, and applications. Elsevier, Lugo. 732 p. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-817943-7.00020-2
- Jiménez, J. y G. Torres. 2023. Diagnóstico de la maricultura en Ecuador: oportunidades y desafíos. AquaTechnica, 5(2), 134–155. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8411400
- Karthikeyan, K. and M. Shanmugam. 2017. The effect of potassium-rich biostimulant from seaweed Kappaphycus alvarezii on yield and quality of cane and cane juice of sugarcane var. Co 86032 under plantation and ratoon crops. J. Appl. Psychol. , 29(6), 3245–3252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-017-1211-6
- Khan, W., U.P. Rayirath, S. Subramanian, M. N. Jithesh, P. Rayorath, D. M. Hodges, A. T. Critchley, J. S. Craigie, J. Norrie and B. Prithiviraj. 2009. Seaweed extracts as biostimulants of plant growth and development. J. Plant Growth Regul., 28(4): 386–399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-009-9103-x
- Klejdus, B., L. Lojková, M. Plaza, M. Šnóblová and D. Štěrbová. 2010. Hyphenated technique for the extraction and determination of isoflavones in algae: Ultrasound-assisted supercritical fluid extraction followed by fast chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Cromatogr. A., 1217(51): 7956–7965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2010.07.020
- Lawanyawut, K., S. Warotaipan and A. Kaewkong. 2002. Nutritional composition and Ca, P and Fe quantities of seaweed in Thailand. Fish. Sci., 68:1321–1322. https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/fishsci1994/68/sup2/68_sup2_1321/_pdf
- Layek, J., A. Das, R. G. Idapuganti, D. Sarkar, A. Ghosh, S. T. Zodape, R. Lal, G. S. Yadav, A. S, Panwar, S. Ngachan and R. S. Meena. 2018. Seaweed extract as organic bio-stimulant improves productivity and quality of rice in eastern Himalayas. J. Appl. Phycol., 30(1): 547–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-017-1225-0
- Leandro, A., D. Pacheco, J. Cotas, J. C. Marques, L. Pereira and A. M. M. Gonçalves. 2020. Seaweed’s bioactive candidate compounds to food industry and global food security. Life, 10(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/life10080140
- Lema Ch., E., I. Chóez-Guaranda, O. Ruíz-Barzola, L. I. Jaramillo, A. Pacheco Flores de Valgaz, S. Van Den Hende y P. Manzano Santana. 2023. Estudio de la variabilidad en el tiempo y espacio de la actividad antioxidante y composición bioquímica de Kappaphycus alvarezii en diferentes densidades de siembra. Rev. Bionatura, 8(1): 1–11. https://doi.org/10.21931/rb/2023.08.01.13
- Mantri, V. A., K. Eswaran, M. Shanmugam, M. Ganesan, V. Veeragurunathan, S. Thiruppathi, C. R. K. Reddy and A. Seth. 2017. An appraisal on commercial farming of Kappaphycus alvarezii in India: success in diversification of livelihood and prospects. J. Appl. Phycol., 29(1): 335–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0948-7
- Matos, G. S., S. G. Pereira, Z. A. Genisheva, A. M. Gomes, J. A. Teixeira and C. M. R. Rocha. 2021. Advances in extraction methods to recover addedvalue compounds from seaweeds: Sustainability and functionality. Foods, 10(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10030516
- Michalak, I., K. Chojnacka, A. Dmytryk, R. Wilk, M. Gramza and E. Rój. 2016. Evaluation of supercritical extracts of algae as biostimulants of plant growth in field trials. Front. Plant Sci., 7: 1-11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01591
- Mondal, D., A. Ghosh, K. Prasad, S. Singh, N. Bhatt, S. T. Zodape, J. P. Chaudhary, J. Chaudhari, P. B. Chatterjee, A. Seth and P. K. Ghosh. 2015. Elimination of gibberellin from Kappaphycus alvarezii seaweed sap foliar spray enhances corn stover production without compromising the grain yield advantage. Plant Growth Regul., 75(3): 657–666. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-014-9967-z
- Montúfar-Romero, M., R. E. Rincones-León, L. B. Cáceres-Farías, M. M. Espinoza-Vera, U. Avendaño, T. Cruz-Jaime, L. Cubillos, W. Ruiz, W. Revelo, C. Lodeiros, A. Alfaro-Núñez and L. Cáceres-FarÍas. 2023. Feasibility of aquaculture cultivation of elkhorn sea moss (Kappaphycus alvarezii) in a horizontal long line in the Tropical Eastern Pacific. Sci. Rep. , 13(1), 14751. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-41795-x
- Mukherjee, A. and J. S. Patel. 2020. Seaweed extract: biostimulator of plant defense and plant productivity. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol., 17(1), 553–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02442-z
- Murillo Carvajal, R. y R. Romo González. 2021. Diseño de una planta piloto basado en la extracción de bioestimulantes de la macroalga Kappaphycus alvarezii con aplicación al sector agrícola. Tesis Ing. Quim., Esc. Sup. Politécn. Lit., Guayaquil. 60 p. https://www.dspace.espol.edu.ec/bitstream/123456789/52070/3/T-110225 MURILLO Y ROMO.pdf
- Murugaiyan, K. 2020. Seasonal studies on the carbohydrate content of some marine macroalgae in Gulf of Mannar coastal region, India. Trop. Plant Res., 7(3): 684–688. https://doi.org/10.22271/tpr.2020.v7.i3.086
- Noli, Z., A., Suwirmen, Aisyah and P. Aliyyanti. 2021). Effect of liquid seaweed extracts as biostimulant on vegetative growth of soybean. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci., 759(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/759/1/012029
- Pandya, M. and S. Mehta. 2023. Seaweed utilizing as a biostimulants in agriculture sector: a review. Int. J. Res. Appl., 11(3): 927–934. https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.49561
- Patel, K., P. Agarwal and P. K. Agarwal. 2018. Kappaphycus alvarezii sap mitigates abiotic-induced stress in Triticum durum by modulating metabolic coordination and improves growth and yield. J. Appl. Phycol., 30(4): 2659–2673. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-018-1423-4
- Pedro, S. F., K. S. Franco Jr, V. M. Ribeiro y G. P. Brigante. 2022. Efeitos do fertilizante a base de extratos de algas marinhas no crescimento inicial do cafeeiro. Res. Soc. Dev., 11(17): e79111738844. https://doi.org/10.33448/rsd-v11i17.38844
- Pérez-Madruga, Y., I. López-Padrón e Y. Reyes-Guerrero. 2020. Las algas como alternativa natural para la producción de diferentes cultivos. Cult. Trop.,41(2): 9. http://ediciones.inca.edu.cu
- Pramanick, B., K. Brahmachari, B. S. Mahapatra, A. Ghosh, D. Ghosh and S. Kar. 2017. Growth, yield and quality improvement of potato tubers through the application of seaweed sap derived from the marine alga Kappaphycus alvarezii. J. Appl. Phycol., 29(6): 3253–3260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-017-1189-0
- Raju, G., S. Kohila and K. Ramachandiran. 2017. Evaluating the effect of seaweed formulations on the quality and yield of sugarcane. Madras Agric. J.,104(4–6): 4–9. https://doi.org/10.29321/MAJ.04.000423
- Ramu Ganesan, A., K. Subramani, M. Shanmugam, P. Seedevi, S. Park, A. H. Alfarhan, R. Rajagopal and B. Balasubramanian. 2020. A comparison of nutritional value of underexploited edible seaweeds with recommended dietary allowances. J. King Saud Univ. Sci., 32(1): 1206–1211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2019.11.009
- Rana, V., S., K. Lingwal, S. Sharma, N. Rana, R. Pawar, V. Kumar and U. Sharma. 2023. Enhancement in growth, yield and nutritive characteristics of strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) by the application of biostimulant: seaweed extract. Acta Physiol. Plant., 45(10): 1–12. https://doi. org/10.1007/s11738-023-03602-y
- Ravi, I., K. Kamaraju1, S. Kumar and S. Sailaja Nori. 2018. Foliar application of seaweed bio formulation enhances growth and yield of banana cv. grand naine (AAA). IJONS, 8(47): 13482–13488.
- Reka, P., A. Thahira Banu and M. Seethalakshmi. 2017. Elemental composition of selected edible seaweeds using SEM- energy dispersive spectroscopic analysis. Int. Food Res. J., 24(2): 600–606.
- Rodriguez Tenorio, P. A., L. Méndez-Rodríguez, E. Serviere-Zaragoza, T. Hara and T. Zenteno-Savín. 2013. Antioxidant substances and trace element content in macroalgae from a subtropical lagoon in the west coast of the Baja California Peninsula. Vitam. Trace Elem., 2(1): 1–5. https://doi.org/10.4172/2167-0390.1000108
- Rouphael, Y. and G. Colla. 2020. Editorial: Biostimulants in agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. , 11(February), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00040
- Rouphael, Y., M. Giordano, M. Cardarelli, E. Cozzolino, M. Mori, M. C. Kyriacou, P. Bonini and G. Colla. 2018. Plant-and seaweed-based extracts increase yield but differentially modulate nutritional quality of greenhouse spinach through biostimulant action. Agronomy, 8(7), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8070126
- Roy, A., D. Ghosh, M. Kasera, T. R. Girish, S. Nori, R. S. Vemanna, S. Mohapatra, S. S. Narayan and S. Bhattacharjee. 2022. Kappaphycus alvareziiderived formulations enhance salicylic acid-mediated anti-bacterial defenses in Arabidopsis thaliana and rice. J. Appl. Phycol., 34(1): 679–695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-021-02658-y
- Rudke, A. R., C. J. de Andrade and S. R. S. Ferreira. 2020. Kappaphycus alvarezii macroalgae: An unexplored and valuable biomass for green biorefinery conversion. Trends Food Sci. Technol., 103: 214–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.07.018
- Ruiz-Medina, M. A., M. Sansón and A. M. González-Rodríguez. 2022. Changes in antioxidant activity of fresh marine macroalgae from the Canary Islands during air-drying process. Algal Res., 66, 102798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2022.102798
- Samuels, L. J., M. E. Setati and E. H. Blancquaert. 2022. Towards a better understanding of the potential benefits of seaweed based biostimulants in Vitis vinifera L. cultivars. Plants, 11(3), 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11030348
- Seo, U., H. Kang, K. Yoon and Y. An. 2019. Analysis of dietary fiber, mineral content and fatty acid composition in Cheonggak (Codium fragile). Korean J. Food Nutr., 32(4): 328–334. https://doi.org/doi.org/10.9799/ksfan.2019.32.4.328.
- Shah, M. T., S. T. Zodape, D. R. Chaudhary, K. Eswaran and J. Chikara. 2013. Seaweed sap as an alternative liquid fertilizer for yield and quality improvement of wheat. J. Plant Nutr. , 36(2), 192–200. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2012.737886
- Shukla, P. S., T. Borza, A. T. Critchley and B. Prithiviraj. 2021. Seaweed-based compounds and products for sustainable protection against plant pathogens. Mar. Drugs, 19(2): 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19020059
- Shukla, P. S., N. Nivetha, S. S. Nori, D. Bose, S. Kumar, S. Khandelwal, A. Critchley and S. Suryanarayan. 2023. Understanding the mode of action of AgroGain®, a biostimulant derived from the red seaweed Kappaphycus alvarezii in the stimulation of cotyledon expansion and growth of Cucumis sativa (cucumber). Front. Plant Sci., 14(April), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2023.1136563
- Sithamparanathan S., W. K. Balasooriya, S. J. Arasakesary and N. Gnanavelrajah. 2019. Effect of seaweed extract (Kappaphycus alvarezii) on the growth, yield and nutrient uptake of leafy vegetable Amaranthus polygamous. Trop. Agric. Res., 30(3): 81. https://doi.org/10.4038/tar.v30i3.8321
- Suresh Kumar, K., K. Ganesan and P. V. Subba Rao. 2015. Seasonal variation in nutritional composition of Kappaphycus alvarezii (Doty) Doty—an edible seaweed. J. Food Sci. Technol., 52(5): 2751–2760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1372-0
- Tabet, E., R. Al-Haf, C. Hosri, Z. Zind, L. Farah and D. Darazy. 2021. The effect of fertigation and foliar application of seaweed’s biostimulant on banana yield. Agric. Sci., 3(1), p1. https://doi.org/10.30560/as.v3n1p1
- Udayan, A., S. Kathiresan and M. Arumugam. 2018. Kinetin and gibberellic acid (GA3) act synergistically to produce high value polyunsaturated fatty acids in Nannochloropsis oceanica CASA CC201. Algal Res., 32: 182–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2018.03.007
- Uju, N. P. S. U. K. Dewi, J. Santoso, I. Setyaningsih, S. D. Hardingtyas and Yopi. 2020. Extraction of phycoerythrin from Kappaphycus alvarezii seaweed using ultrasonication. IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci., 414(1). 012028. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/414/1/012028
- Vaghela, P., K. Trivedi, K. G. V. Anand, H. Brahmbhatt, J. Nayak, K. Khandhediya, K. Prasad, K. Moradiya, D. Kubavat, L. J. Konwar, V. Veeragurunathan, P. G. Grace and A. Ghosh. 2023. Scientific basis for the use of minimally processed homogenates of Kappaphycus alvarezii (red) and Sargassum wightii (brown) seaweeds as crop biostimulants. Algal Res., 70. 102969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2023.102969
- Valverde-Balladares, P. y H. D. Armas. 2023. Potencial nutracéutico de macroalgas marina–Ecuador. FACSalud UNEMI, 6(11): 42–52.
- Veerman, C., T. Pinto Correia and C. Bastioli. 2020. Caring for soil is caring for life: ensure 75 % of soils are healthy by 2030 for food, people, nature and climat. European Commission, Directorate-General for Research and Innovation. Rep. Mission Board Soil Health Food, Publ. Off., Brussels.82 p. https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2777/821504
- Zakaria, N. A., D. Ibrahim, S. F. Sulaiman and A. Supardy. 2011. Assessment of antioxidant activity, total phenolic content and invitro toxicity of Malaysian red seaweed, Acanthophora spicifera. J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 3(1): 675–684.
- Zodape, S., T., A. Gupta, S. C. Bhandari, U. S. Rawat, D. R. Chaudhary, K. Eswaran and J. Chikara. 2011. Foliar application of seaweed sap as biostimulant for enhancement of yield and quality of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.). J. Sci. Ind. Res. , 70(3): 215–219.