Immunotoxicity and lysosomal damage on Pinctada imbricata (Röding) exposed to used automobile crankcase oils
Published 2024-01-01
Keywords
- Hemocyte; lysosomal destabilization; oil; immunology; stress
How to Cite
Copyright (c) 2023 Edgar Alexander Zapata Vivenes, Gabreial Sanchez, Leida Marcano

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Abstract
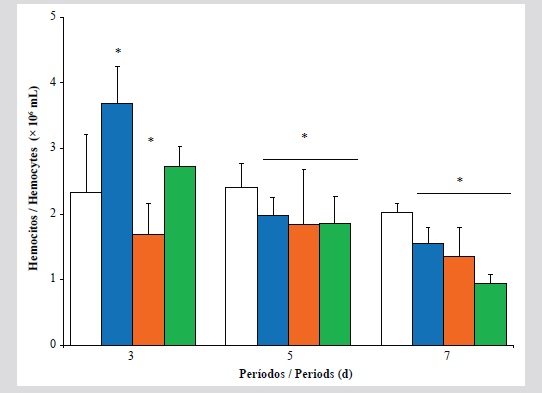
The effect of exposure to water-soluble fractions of used automobile crankcase oils (WSF-AUCO) on haematology parameters, immune system, stability of lysosomal membranes of hemocytes and lipid peroxidation in the digestive gland of the pearl oyster Pinctada imbricata was evaluated in this study. The oysters were exposed to 0, 1, 10 and 20 % v/v of WSF-AUCO during different periods: 3, 5 and 7 d, in static aquaria under controlled conditions (oxygenation 6 mg/L; 25 ± 1 °C; pH 8.0 and 36 ‰). During the early period (3d) of exposure, an increase in the total count of hemocytes (TCH) was observed to 10 % of WSF-AUCO. In oyster exposed to 20 % during 7 d significant decreases in immuno-hematological parameters associated with high lysosomal destabilization of hemocytes
and malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration was observed. The oysters showed compensatory cellular responses to the WSF-AUCO low concentrations, but these decreased during acute exposure. Immuno-modulator effects were induced by complex mixtures of compounds of WSF-AUCO. The molecular and immune-cellular responses estimated in P. imbricada offer appropriate information on the change in
the normal physiology of organisms that inhabit impacted environments by complex mixtures of xenobiotics.
Downloads
References
- Aliko, V., G. Hajdaraj, A. Caci and C. Faggio. 2015. Copper induced lysosomal membrane destabilisation in haemolymph cells of mediterranean green
- crab (Carcinus aestuarii, Nardo, 1847) from the Narta Lagoon (Albania). Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 58(5):750–756. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1516-
- Allam, B. and D. Raftos. 2015. Immune responses to infectious diseases in bivalves. J. Invert. Pathol., 131: 121–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jip.2015.05.005
- Auguste, M., Balbi, T., Ciacci, C., Canonico, B., Papa, S., Borello, A., Vezzulli, L., Canesi, L. 2020. Shift in immune parameters after repeated exposure to
- nanoplastics in the marine bivalve Mytilus. Front Immunol. 15: 11:426. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.00426
- Auguste, M., T. Balbi, C. Ciacci, B. Canonico, S. Papa, A. Borello, L. Vezzulli, L. Canesi, L. 2020. Shift in immune parameters after repeated exposure to
- nanoplastics in the marine bivalve Mytilus. Front Immunol. 15: 11:426. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.00426
- Bachère, E., R.D. Rosa, P.M. Schmitt, A. Poirier and N. Merou. 2015. The new insights into the oyster antimicrobial defense: cellular, molecular and genetic
- view. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2015, 46 (1), pp.50-64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2015.02.040
- Balbi, T., M. Auguste, C. Ciacci and L. Canesi. 2021. Immunological Responses of Marine Bivalves to Contaminant Exposure: Contribution of the -Omics
- Approach. Front Immunol. 12: 618726. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.618726
- Basria, S.M.N., R.I. Mydin and S. Okekpa. 2019. Reactive oxygen species, cellular redox homeostasis and cancer. homeostasis–an integrated vision. In:
- Lasacosvitsch F, S. Dos Anjos Garnes (Eds) BiotechOpen, London. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.76096
- Burgos-Aceves, M. A. and C. Faggio. 2017. An approach to the study of the immunity functions of bivalve haemocytes: Physiology and molecular aspects.
- Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 67, 513–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.06.042
- Cvengros, J., T. Liptaj and N. Pónayová. 2017. Study of polyaromatic hydrocarbons in current used motor oils, Int. J. Petrochem. Sci. Eng., 2(7) 219-226.
- https://doi.org/10.15406/ipcse.2017.02.00060
- Freitas, J.S., T.S. Boscolo-Pereira, C.N. Pereira-Boscolo, M. Navarro-García, C.A. de Oliveira-Rivero and E.A. De Almeida. 2020. Oxidative stress,
- biotransformation enzymes and histopathological alterations in Nile tilapia (Orechromis niloticus) exposed to new and used automotive lubricant oil.
- Comp. Physiol., 234: 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2020.108770
- Goven, A. and J. Kennedy. 1996. Environmental pollution and toxicity in invertebrates: An earthworm model for immunotoxicology. Adv. Comp. Environ.
- Physiol., 24: 170-211. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-79847-4_7
- He, L., T. He, S. Farrar, L. Ji, T. Liu and X. Ma. 2017. Antioxidants maintain cellular redox homeostasis by elimination of reactive oxygen species. Cell
- Physiol. Biochem., 44: 532-553. https://doi.org/10.1159/000485089
- Hwang, H.M., B. Stanton, T. Mcbride and M. Anderson. 2014. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon body residues and lysosomal membrane destabilization
- in mussels exposed to the Dubai Star bunker fuel oil (intermediate fuel oil 380) spill in San Francisco Bay. Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 33: 1117–1121.
- https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2518
- Jiang Y, Tang X, Sun T, Wang and Y. BDE-47 Exposure Changed the Immune Function of Haemocytes in Mytilus edulis: An Explanation Based on ROSMediated
- Pathway. Aquat Toxicol (2017) 182:58–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.11.010
- Liao, Y., C. Cai, C. Yang, Z. Zheng, Q. Wang, X. Du and Y. Deng. 2020. Effect of protein sources in formulated diets on the growth, immune response, and
- intestinal microflora of pearl oyster Pinctada fucata martensii. Aquac. Rep., 16: 100253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2019.100253
- Lodeiros, C.J., L. Freites, A. Márquez, M.E. Glem, M. Guevara and P.E. Saucedo. 2016. Comparative growth and survival of spat of the Caribbean pearl oyster,
- Pinctada imbricata cultivated indoor with microalgae diets and outdoor with natural diet. Aquacul. Nutr., 23(3): 511–522. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12419
- López-Landavery, E.A., G. Amador-Cano, M.A. Tripp-Valdez, N. Ramírez-Álvarez, F. Cicala, R.J.E. Gómez-Reyes, F. Díaz, A.D. Re-Araujo and C.E.
- Galindo-Sánchez. 2022. Hydrocarbon exposure effect on energetic metabolism and immune response in Crassostrea virginica. Marine Pollution Bulletin.
- :113738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.113738.
- Lowe, D., M. Moore and B. Evans. 1992. Contaminant impact of interactions of molecular probes with lysosomes in living hepatocytes from dab Limanda
- limanda. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 91 (1): 135-140. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps091135
- Lowry, O., N. Rosebroungh, A. Farr and R. Randall. 1951. Protein measurement with the folin reagent. J. Biol. Chem., 193: 265-275.
- Mansour, C., F.B. Taheur and R. Omrani. 2020. Immune biomarker and hydrocarbon concentrations in carpet shell clams (Ruditapes decussatus) collected
- from a Mediterranean coastal lagoon. Euro-Mediterr J. Environ. Integr., 5: 11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-020-0147-4
- Martínez-Gómez, C., J. Benedicto, J.A. Campillo and M. Moore. 2008. Application and evaluation of the neutral red retention (NRR) assay for lysosomal
- stability in mussel populations along the Iberian Mediterranean coast. J. Environ. Monit., 10(4): 490. https://doi.org/10.1039/b800441m
- Matozzo, V., M. Giacomazzo, L. Finos, M.G. Marin, L. Bargelloni and M. Milan. 2013. Can ecological history influence immunomarker responses and
- antioxidant enzyme activities in bivalves that have been experimentally exposed to contaminants? A new subject for discussion in “eco-immunology”
- studies. Fish Shell. Immunol., 35(1): 126–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2013.04.013
- Méthé, D., L.A. Comeau, H. Stryhn, J.F. Burka, T. Landry and J. Davidson. 2017. Haemolymph fluid osmolality influences the neutral-red retention assay
- in the eastern oyster Crassostrea virginica, J. Molluscan Stud. 83: 229–234. https://doi.org/10.1093/mollus/eyw050
- Nusetti, O., L. Marcano, E. Zapata, M. Escalpés, S. Nusetti y C. Lodeiros. 2004. Respuestas inmunológicas y de enzimas antioxidantes en la ostra perla Pinctada
- imbricata (Mollusca: Pteridae) expuesta a niveles subletales de fuel oil Nº6. Interciencia, 29(6): 324-328. http://ve.scielo.org/scielo.php?script=sci_
- arttextypid=S0378-18442004000600008ylng=esynrm=iso
- Ohkawa, H., N. Ohishi and K. Yagi. 1979. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction, Rev. Anal. Biochem. 95: 351–358.
- https:// doi. org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738
- Olonisakin, A., A. Adebayo and M.O. Aremu. 2005. Metal concentrations of fresh, used and treated crankcase oil. Biosci. Biotech. Res. Asia; 3: 187-191.
- Available from: http://www.biotech-asia.org/?p=4361
- Parisi, M.G., J. Pirrera, C.M. La Corte, D. Dara, M. Parrinello and Cammarata. 2021. Effects of organic mercury on Mytilus galloprovincialis hemocyte
- function and morphology. J. Comp. Physiol. B; 191: 143–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-020-01306-0
- Renault, T. 2015. Immunotoxicological effects of environmental contaminants on marine bivalves. Fish Shellfish Immunol., 46(1): 88–93. https://doi.
- org/10.1016/j.fsi.2015.04.011
- Romero-Fereira, P., D. Arrieche, V. Acosta, L. Pérez and C. Lodeiros. 2017. Gametogenic cycle of the oyster, Pinctada imbricata, in suspended culture in
- the Gulf of Cariaco, Venezuela. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res.;45(1): 139-148. https://doi.org/10.3856/vol45-issue1-fulltext-13
- Sun, S., W. Shi, Y. Tang, Y. Han, X. Du, W. Zhou, Y. Hu, C. Zhou and G. Liu. 2020. Immunotoxicity of petroleum hydrocarbons and microplastics alone
- or in combination to a bivalve species: Synergic impacts and potential toxication mechanisms. Sci. Total Environm., 728: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.
- scitotenv.2020.138852
- Strober, W. 2015. Trypan blue exclusion test of cell viability. Curr. Protoc. Im. 2 111, https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142735.ima03bs111
- Sokal, R. and F. Rohlf. 2012. Biometry. 4th Ed. W.H. Freeman. New York.
- Trivedi, P.C., J.J. Bartlett and T. Pulinilkunnil. 2020. Lysosomal biology and function: Modern view of cellular debris bin. Cells, 9(5): 1131. https://
- doi. org/10.3390/cells9051131
- Vásquez, G., R. Crescini, W. Villalba, J. Mogollón y L. Troccoli. 2015. Aspectos biológicos básicos de Pinctada imbricata (Bivalvia: Pteriidae) en la laguna
- de La Restinga, isla de Margarita, Venezuela. Rev, Cienc. Mar. Cost.,7: 117-132. https://doi.org/10.15359/revmar.7.8
- Villegas, L., C. Lodeiros, K. Malavé, J. Revilla y M. Lemus. 2015. Efecto subletal del cadmio en la ostra perla del Caribe Pinctada imbricata (Pteroida:
- Pteriidae) Röding, 1798. Saber; 27 (1): 39-45
- Week, J., V. Sharp and T. Williams. 1997. Contaminant-induced lisosomal membrane damage in blood cells of green mussel Perna viridis (Mytilidae): a
- field transplant study. Technical Report WC/97/64. DFID-TDR Proyect R6191. Land-derived contaminant influx to Jakarta Bay, Indonesia; 2: 1-30.
- Wei J., B Liu, S Fan, B Zhang, J Su and D. Yu. 2017. Serum immune response of pearl oyster Pinctada fucata to xenografts and allografts. Fish Shellfish
- Immunol., 62: 303-310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.01.039
- Xie, J., C. Zhao, Q. Han, H. Zhou, Q. Li and X. Diao. 2017. Effects of pyrene exposure on immune response and oxidative stress in the pearl oyster, Pinctada
- martensii. Fish Shellfish Immunol., 63: 237–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.02.032
- Zha, S., J. Rong, X. Guan, Y. Tang, Y. Han and G. Liu. 2019. Immunotoxicity of four nanoparticles to a marine bivalve species, Tegillarca granosa. J. Hazard
- Mater 377:237–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.05.071
- Zannella, C., F. Mosca, F. Mariani, G. Franci, V. Folliero, M. Galdiero, P.G. Tiscar and M. Galdiero. 2017. Microbial diseases of bivalve mollusks: infections,
- immunology and antimicrobial defense. Mar. Drugs; 15(6):182. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15060182
- Zapata-Vívenes, E., L. Marcano y V. Acosta 2018. Respuestas inmunológicas, estabilidad lisosomal y frecuencia de micronúcleos en Eurythoe
- complanata (Polychaeta:Amphinomidae) expuestos a una fracción acuosa de lubricantes usados de motores de automóviles. Rev. Intern. Contam.
- Amb., 34 (2): 297-305. https://doi.org/10.20937/RICA.2018.34.02.10
- Zapata-Vívenes, E., O. Nusetti, L. Marcano, G. Sánchez and H. Guderley. 2020. Antioxidant defenses of flame scallop Ctenoides scaber (Born, 1778) exposed
- to the water-soluble fraction of used vehicle crankcase oils. Toxicol. Rep., 7:1597–1606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.11.009
- Zapata Vívenes, E., G. Sánchez, O. Nusetti and L. Marcano. 2022. Modulation of innate immune responses in the flame scallop Ctenoides scaber (Born,
- caused by exposure to used automobile crankcase oils, Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 130: 342- 349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2022.09.020
- Zhao, C., L. Xiaoxu, L. Shibin and Y. Chang. 2011. Assessments of lysosomal membrane responses to stresses with neutral red retention assay and its potential
- application in the improvement of bivalve aquaculture. Afr, J. Biotechnol., 10 (64): 13968- 3973. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB10.2283
- Zheng, F., F. Marques Gonçalves, Y. Abiko, H. Li, Y. Kumagai and M. Aschner. 2020. Redox toxicology of environmental chemicals causing oxidative stress.
- Redox Biol., 34: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101475